If you’re responsible for operating commercial motor vehicles in the USA, it’s vital that you understand the US ELD mandate and what this means for you and your business.
The ELD mandate is a federal law that was introduced for businesses to prioritize driver safety. This legislation requires you to install electronic logging devices (ELDs) in your vehicles. As of 2019, all commercial motor carriers must have an electronic logging device fitted in accordance with federal law – failure to comply can result in significant fines and penalties.
Whether you’re a fleet manager, owner, operator, or driver, it’s important that you understand the FMCSA ELD mandate and how you and your business can remain compliant with federal law. Below, we’ll cover exactly what the ELD mandate is and the steps you can take to remain compliant.
What is an ELD?
An electronic logging device, often known as an ELD, is a telematics device that integrates with your vehicle’s engine to record driving activity. It’s used by commercial motor vehicle drivers to automatically record driving time and Hours of Service (HOS) records and to capture vehicle-specific data about the engine and miles driven.
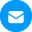
When it comes to fleet management and compliance, an ELD is used to inform fleet managers of drivers’ statuses in real time. This information can then be automatically logged in your fleet management software of choice, for you to review, run reports, and keep track of your fleet.
BigRoad ELD, our electronic logging solution powered by Powerfleet (formerly Fleet Complete) is a leading ELD provider in North America. With an ELD, you can wave goodbye to manual data entry and time-consuming paperwork, and know that your regulatory compliance is taken care of.
What is the ELD mandate?
So, what is the ELD mandate exactly? Since 1938, Hours of Service (HOS) laws have put limits on driver activity to ensure driver safety, particularly around the number of working hours drivers are allowed to perform between rest periods. The first federal law that required U.S. commercial drivers to record their hours of service was passed in 1937, originally in logbooks. The ELD mandate is a federal law requiring drivers to replace paper logs and Automatic On-Board Recording Devices (AOBRD) with automated ELDs. As you can expect, paper logs aren’t always accurate – especially if drivers are tired and overworked which can lead to miscalculations. With this in mind, the ELD mandate was introduced to replace manual paper logs with electronic, automatic recordings for improved accuracy and to minimize road accidents as a result of overworking and driver fatigue.
The ELD mandate applies to most drivers and owner-operators who are required to keep records of duty status (RODS).
However, it’s important to note that there are exemptions to keeping RODS and having ELDs in your fleet’s vehicles. The following may be exempt:
- Short-haul drivers: Drivers who meet the FMCSA’s definition of short-haul driving – operating within a radius of 150 air miles (or 172.6 land miles) of their work reporting location.
- Eight days or fewer: If a driver has eight days or fewer in a month whereby they’re required to complete the RODS, they are exempt from the ELD mandate. Should they need to complete the RODS, they can do so manually or with an AOBRD.
- Vehicles manufactured before the year 2000: Your drivers may keep their RODSs manually or with an AOBRD if their vehicle’s model year is before the year 2000. You can find the date of manufacture in the vehicle’s registration.
- Drive-away-tow-away: If your drivers are conducting a drive-away-tow-away operation, whereby the vehicle being driven is the commodity being delivered, or if the vehicle being transported is a recreational vehicle trailer or motorhome, you may be exempt from the ELD rule.
Why was the ELD mandate introduced?
As we mentioned earlier, Hours of Service (HOS) laws were first introduced to reduce driver accidents caused by driving fatigue, including falling asleep at the wheel and causing crashes, injuries, and deaths. The ELD mandate is one of the most significant outcomes of the Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act, which was signed into law by President Obama in 2012. This made it a legal requirement for every commercial driver in America to record their hours of service through an electronic logging device (ELD).
The ELD mandate was introduced to replace existing logging methods such as paper logs and AOBRDs for improved accuracy, as well as to prevent employers from violating hours of service laws.
What is ELD compliance?
ELD compliance is the process of adhering to the regulations set by government authorities, such as the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). ELD compliance ensures accurate and reliable tracking of driving hours and rest breaks to promote driver safety and prevent driver fatigue. Ensuring your fleet’s vehicles are fitted with ELDs can alleviate some of the pressures surrounding compliance, as your device will automatically record and log data for you.
ELD compliance is there to protect drivers and prioritize driver safety, so the penalties for non-compliance are significant. ELD violation fines can range from $1,000 to $10,000, and non-exempt drivers can be put ‘out of service’ meaning the vehicle or driver cannot operate until certain safety issues or violations have been resolved. With these penalties in mind, you’ll want to ensure you have reliable ELDs in place to protect not only your drivers, but your reputation too.
ELD checklist for drivers
We’ve put together this simple checklist that drivers should keep on hand to ensure their vehicle passes a compliance inspection:
- Driver identification: Perhaps an obvious one, but make sure you carry valid identification documents such as your driver’s license and your commercial driver’s license (CDL).
- ELD user manual: Make sure you have a copy of the ELD user manual in case you need to troubleshoot any issues during an inspection. According to the FMCSA, it’s mandatory that you carry your user manual, instruction sheet for transferring HOS records to safety officials, instruction sheet on reporting ELD malfunctions, and a supply of paper tracking forms for at least eight days should your ELD fail. You’ll also be responsible for providing blank log forms. Your user manual, instruction sheet for transferring HOS records and instruction sheet on reporting malfunctions can all be found in the BigRoad ELD mobile app, so they’re always on hand.
- Vehicle registration: Remember to have the current vehicle registration documents available.
- Insurance documentation: Have copies of the vehicle insurance policy and other relevant insurance documents available should you need them.
ELD checklist for fleet managers
As a fleet manager, you’ll want the reassurance that your vehicle will pass a roadside inspection with no issues. Here is a checklist of items you should keep on hand as a fleet manager when it comes to ELD compliance:
- Fleet information: Keep your records up-to-date with all the vehicles in the fleet, your vehicle identification numbers and registration information.
- ELD vendor information: Make sure you have the contact information for your ELD provider on hand so you know who to call should you face any technical issues.
- Training records: Make sure you maintain your driver training session records on ELD usage so you have evidence of fleet training.
How does the ELD mandate impact Hours of Service (HOS)?
HOS details the amount of time that drivers are authorized to be driving and on duty. To protect the welfare and safety of drivers, they are limited in the number of hours they can drive per day and within a week, which varies depending on whether they are property-carrying or passenger-carrying drivers. The FMCSA explains the HOS regulations in greater detail here.
It’s important to note that the ELD mandate doesn’t change HOS requirements. The main difference is that proof of businesses complying with HOS requirements must come through an ELD, to ensure accurate reporting. Drivers must use an ELD to input their duty status as either driving, on duty but not driving, off duty, or using a sleeping berth.
The benefits of using an ELD
As well as ensuring fleet compliance, ELDs can offer numerous benefits including:
- Improved safety: Using an ELD offers accurate insight into driver hours and ensures drivers are taking rest breaks which can help to prevent driver fatigue – a significant cause of road accidents.
- Efficient processes: ELDs automate record-keeping and allow you to spend time on other tasks rather than the hassle of admin. This allows drivers to focus on driving rather than manually filling out paper logs.
- Real-time monitoring: ELDs offer real-time monitoring for fleet managers to track vehicles, monitor driver behavior, and be alerted should safety be at risk.
- Faster inspections: ELDs speed up the roadside inspection process by providing electronic access to driver logs, for inspectors to quickly review.
- Environmental impact: ELDs can help to lower fuel consumption and emissions by promoting more efficient driving behavior and reducing idling time. This contributes to your business’ sustainability practices and can save your business money on fuel too.
Get ELD compliant today
Powerfleet’s (formerly Fleet Complete) ELD compliance solution ticks all the boxes for improved driver safety and fleet compliance. Improve the accuracy of your data reporting and streamline your processes with a reliable ELD compliance solution.
Book a demo with us today to get started.